Semi-hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes plays a critical role in petrochemical industry, pharmaceutical synthesis and manufacture of fine chemicals.
Recently, a joint research group from DICP and Xiamen university developed an efficient hydride catalyst for alkynes semi-hydrogenation. High selectivity of alkenes can be achieved by using a calcium palladium complex hydride catalyst. This research work was published in Journal of the American Chemical Society.
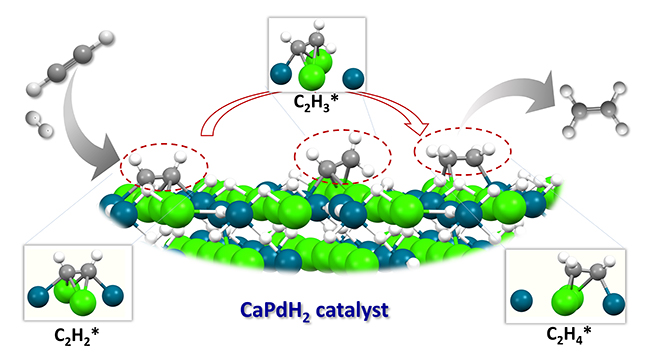
In this study, the research team proposed a new strategy in designing efficient catalysts, and successfully developed CaPdH2 catalysts for alkynes semi-hydrogenation. With the cooperation of [PdH2]δ- and Caδ+ in CaPdH2 structure, high alkene selectivity can be obtained by adjusting the adsorption and hydrogenation barriers of alkynes, alkenes and intermediates. This unique structure of active sites, which is distinguished from the published heterogeneous catalysts, also resulted in fundamentally different reaction pathways and kinetic properties. This research work enriches the catalysts for alkynes selective hydrogenation. What’s more, given the rich family of transition metal complex hydrides, this work may open a new avenue in searching more efficient catalysts for alkynes hydrogenation.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS, and the Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program. (Text by Qing Guo)
Article link:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.1c09489

