Recently, Professor Chen Ping, Professor Guo Jianping and doctoral student Wang Qianru were invited to write a review article on "Future Energy " entitled "The Power of Hydrides".
Hydrogen is the earliest element in the universe and has played a vital role in the universe's evolution and human understanding of the material world. Hydrogen can obtain electrons from more electropositive elements or groups to form hydrides containing negative hydrogen species (H-). These hydrides in the form of molecules, clusters, surface species,or bulk materials have the characteristics of high energy, strong reducibility, and high activity, and show unique efficacy in clean energy storage and utilization and chemical conversion.
Hydride is a hydrogen/ energy carrier and has long been the research object of hydrogen storage and heat storage materials forresearchers in materials science. The H- ion radius is close tothat of O2-, but it has less charge, special coordination, and is easy to polarize. This makes some hydrides able to conductions such as Li+, Na+, and H-, making them potential solid electrolytes. Recently, Researchers have revealed the encouraging result that hydrides can be used as high-temperature superconductors.
The key to sustainable development of clean energy is to convert stable small molecules (such as H2O, CO2, and N2) into energy carriers (such as H2, CH3OH, HCOOH, and NH3) by injecting energy in the form of heat, electricity, and light. Hydrogen production reactions, N2 and CO2 reduction reactions usually require the input of electrons, protons, and energy. Hydrides, which are very active interms ofchemical properties, can participate in these challenging and important reactions through the mutual conversion of H-, HO, and H+. For example, hydrides can serve as a common source of protons and electrons, playing an irreplaceable role in multiphase, biological, and homogeneous nitrogen fixation processes.
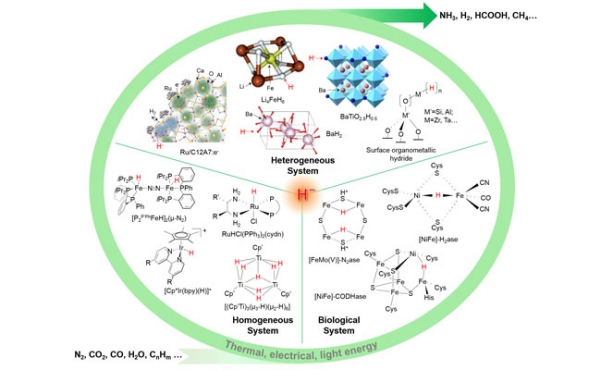
In addition to the powerful functions in the aforementioned fields related to clean energy utilization, hydrides have demonstrated initial application potential in neutron shielding, light capture, and the contentious topic of cold nuclear fusion. The exploration and utilization of hydrides by researchers continue, and the future looks promising.
As a forward-looking platform of Joule, "Future Energy" focuses on research are as that have the potential to develop into new generation technologies and is written by experts in the relevant fields. Professor Chen Ping's team has focused on the research of hydrides for hydrogen storage (Nature, 2002; Nat. Mater., 2008; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019) and catalytic conversion (Nat. Chem., 2017; Nat. Energy, 2018) for nearly 20 years, and has recognized and enriched the connotation and function of hydrides.
The review was published in Joule. The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. (Text/Photo by Wang Qianru).

 Home
>>
Highlights
Home
>>
Highlights